ARP Traffic
ARP Overview
ARP or Address Resolution Protocol is a Layer 2 protocol that is used to connect IP Addresses with MAC Addresses. They will contain REQUEST messages and RESPONSE messages. To identify packets the message header will contain one of two operation codes:
Request (1)
Reply (2)
Below you can see a packet capture of multiple ARP requests and replies.
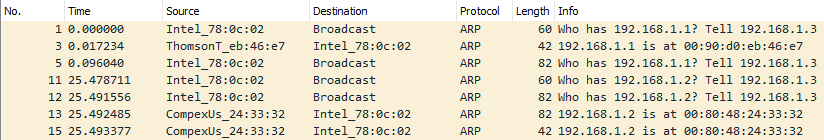
It is useful to note that most devices will identify themselves or Wireshark will identify it such as Intel_78, an example of suspicious traffic would be many requests from an unrecognized source. You need to enable a setting within Wireshark however to resolve physical addresses. To enable this feature, navigate to View > Name Resolution > Ensure that Resolve Physical Addresses is checked.
Looking at the below screenshot we can see that a Cisco device is sending ARP Requests, meaning that we should be able to trust this device, however you should always stay on the side of caution when analyzing packets.
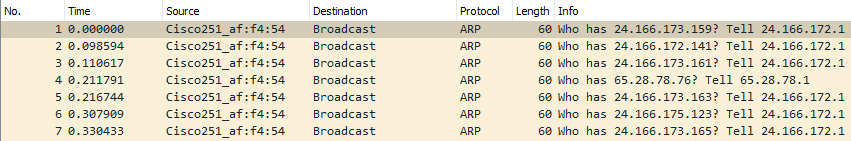
ARP Traffic Overview
ARP Request Packets:
We can begin analyzing packets by looking at the first ARP Request packet and looking at the packet details.
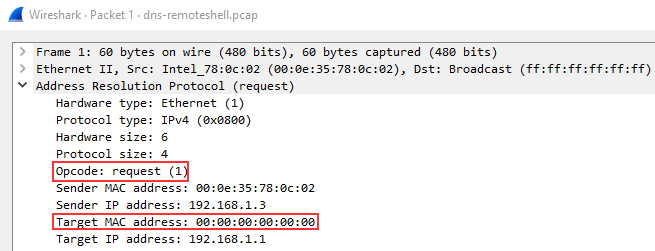
Looking at the packet details above, the most important details of the packet are outlined in red. The Opcode is short for operation code and will you tell you whether it is an ARP Request or Reply. The second outlined detail is to where the packet is requesting to, in this case, it is broadcasting the request to all.
ARP Reply Packets:

Looking at the above packet details we can see from the Opcode that it is an ARP Reply packet. We can also get other useful information like the MAC and IP Address that was sent along with the reply since this is a reply packet we know that this was the information sent along with the message.
ARP is one of the simpler protocols to analyze, all you need to remember is to identify whether it is a request or reply packet and who it is being sent by.
Practical ARP Packet Analysis
Now that you know what ARP packets and normal traffic look like download the provided PCAP or nb6-startup.pcap from the Wireshark website. This capture has multiple protocols so you may need to use your knowledge of filtering from previous tasks; once you're ready, begin analysis of the capture.
What is the Opcode for Packet 6?
What is the source MAC Address of Packet 19?
What 4 packets are Reply packets?
What IP Address is at 80:fb:06:f0:45:d7?
Last updated