Packet Dissection
This section covers how Wireshark uses OSI layers to break down packets and how to use these layers for analysis. It is expected that you already have background knowledge of what the OSI model is and how it works.

Raza, M., 2018. 7 Layers Of The OSI Model
Packet Details
You can double click on a packet in capture to open its details. Packets consist of 5 to 7 layers based on the OSI model. We will go over all of them in an HTTP packet from a sample capture.

Looking above we can see 7 distinct layers to the packet: frame/packet, source [MAC], source [IP], protocol, protocol errors, application protocol, and application data. Below we will go over the layers in more detail.
Frame (Layer 1) -- This will show you what frame / packet you are looking at as well as details specific to the Physical layer of the OSI model.

Source [MAC] (Layer 2) -- This will show you the source and destination MAC Addresses; from the Data Link layer of the OSI model.

Source [IP] (Layer 3) -- This will show you the source and destination IPv4 Addresses; from the Network layer of the OSI model.
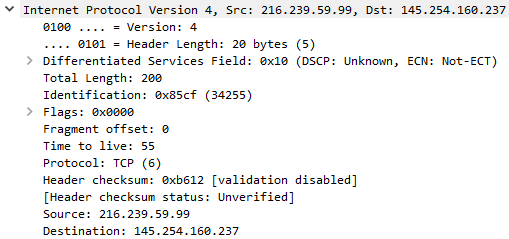
Protocol (Layer 4) -- This will show you details of the protocol used (UDP/TCP) along with source and destination ports; from the Transport layer of the OSI model.
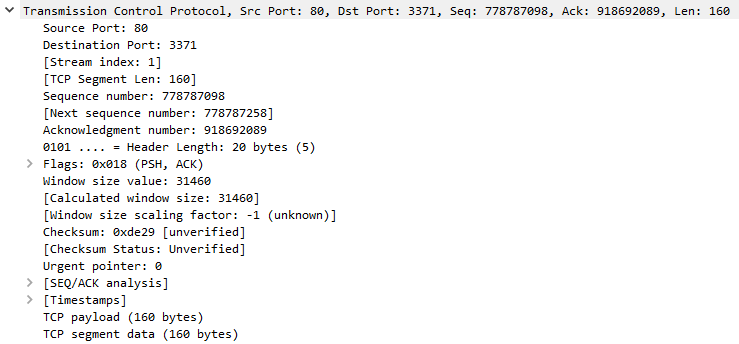
Protocol Errors -- This is a continuation of the 4th layer showing specific segments from TCP that needed to be reassembled.

Application Protocol (Layer 5) -- This will show details specific to the protocol being used such HTTP, FTP, SMB, etc. From the Application layer of the OSI model.
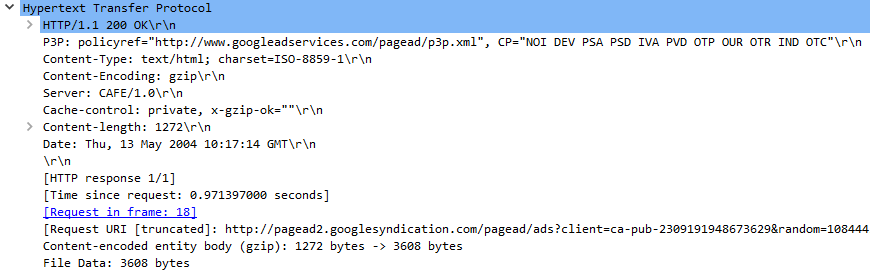
Application Data -- This is an extension of layer 5 that can show the application-specific data.

Now that we understand what a general packet is composed of, move on to looking at various application protocols and their specific details.
Read the above and move on to analyzing application protocols.
Last updated